Definition of Hooke's Law in Physics
It could deform like a solid according to Hookes law F kx. In physics mass is not the same as weight even though mass is often.
Newtons law of universal gravitation is usually stated as that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.

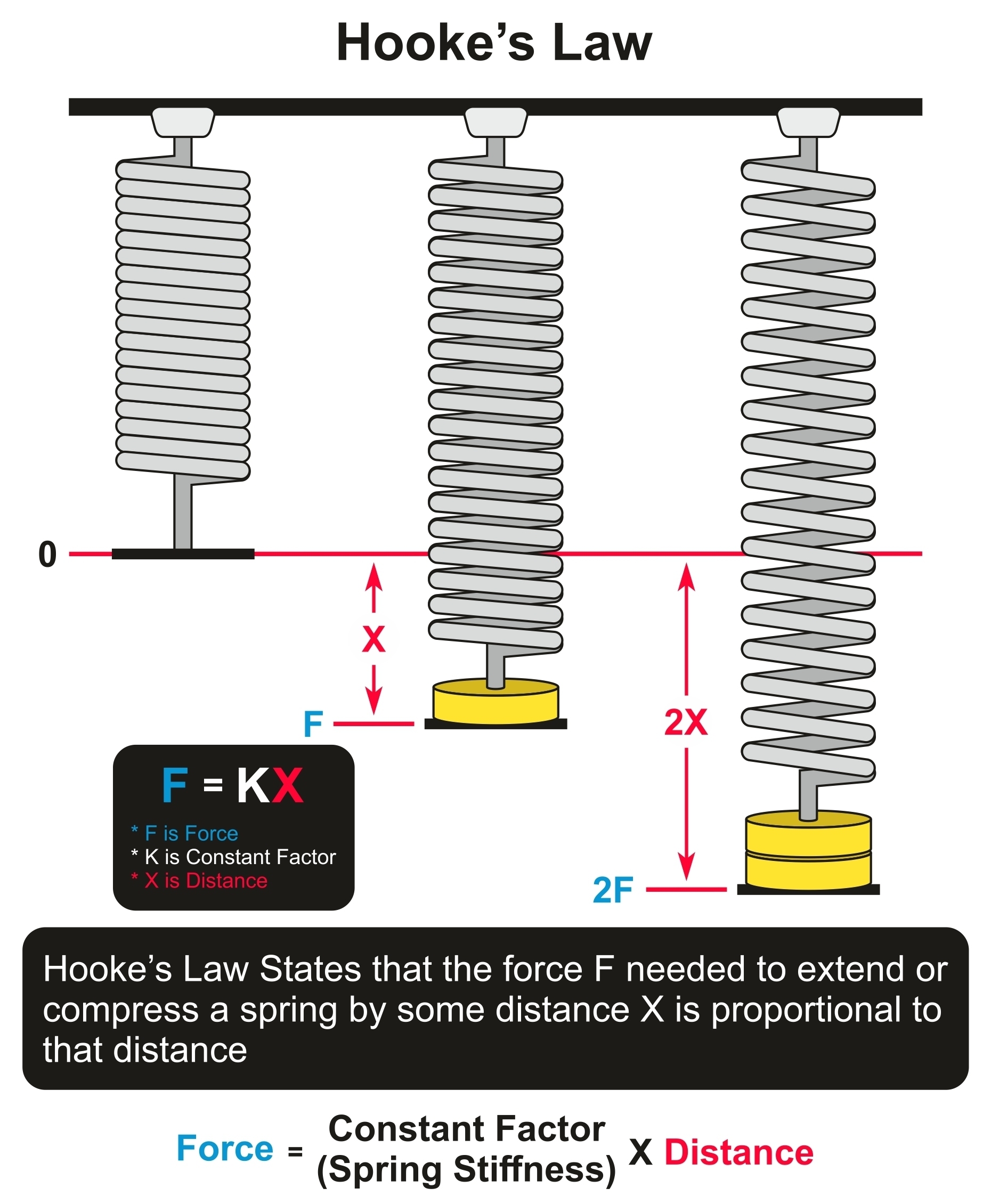
. In physics Hookes law is an empirical law which states that the force F needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance x scales linearly with respect to that distancethat is F s kx where k is a constant factor characteristic of the spring ie its stiffness and x is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. If a weight W mg is hung from one end of an ordinary spring causing it to stretch a distance x then an equal and opposite force F is created in the spring which opposes the pull of the weight. Plasma is called the fourth state of matter after solid liquid and gas.
F is the force applied in newtons N. In the continuum mechanics of solids the second law of thermodynamics is satisfied if the ClausiusDuhem form of the entropy inequality is satisfied. It is a state of matter in which an ionized substance becomes highly electrically conductive to the point that long-range electric and magnetic fields dominate its behaviour.
This law states that. Hookes law basically states that when an object has a relatively small deformation the size of the deformation is directly. F is the force and x is the change in springs.
Hookes Law Experiment Objective. Its scope of study encompasses not only the behaviour of objects. K -Fx where k is the spring constant.
When the block moves away from the wall horizontally spring tries to restore and due to this oscillatory motion starts. That symbol f makes it look like were discussing static friction. The restoring force by the spring is directly proportional to the change in the position and is directed towards the mean position Spring Constant Formula.
Elasticity ability of a deformed material body to return to its original shape and size when the forces causing the deformation are removed. Up to a certain limit only the stress is directly proportional to strain. In this portion Hookes law is being obeyed by the material of the wire.
When English scientist Robert Hooke was studying springs and elasticity in the 19th century he observed that numerous materials had a similar feature when the stress-strain connection was analysed. R is the distance in meters from the pivot point to where the force is applied. Hookes law equation provides the given expression for.
If W is not so large as to permanently distort the. The formula to calculate the spring constant is as follows. The first constitutive equation constitutive law was developed by Robert Hooke and is known as Hookes law.
It could get stuck F f. It relates stress force per unit area to strain proportional deformation along an axis or lineThe basic principle is that a material undergoes elastic deformation when it is compressed or extended returning to its original shape when the load is removed. It encompasses the study of the conditions under which fluids are at rest in stable equilibrium as opposed to fluid dynamics the.
Definitions The fourth state of matter. In the broadest sense physics from the Greek physikos is concerned with all aspects of nature on both the macroscopic and submicroscopic levels. Hookes Law defined a linear zone in which the force required to stretch material was proportionate to the extension of the material.
The stress-strain curve is the relationship between stress and corresponding strain. Although the term fluid generally includes both the liquid and gas phases its definition varies among branches of. The publication of the theory has become known as the first great unification as it marked the unification of the.
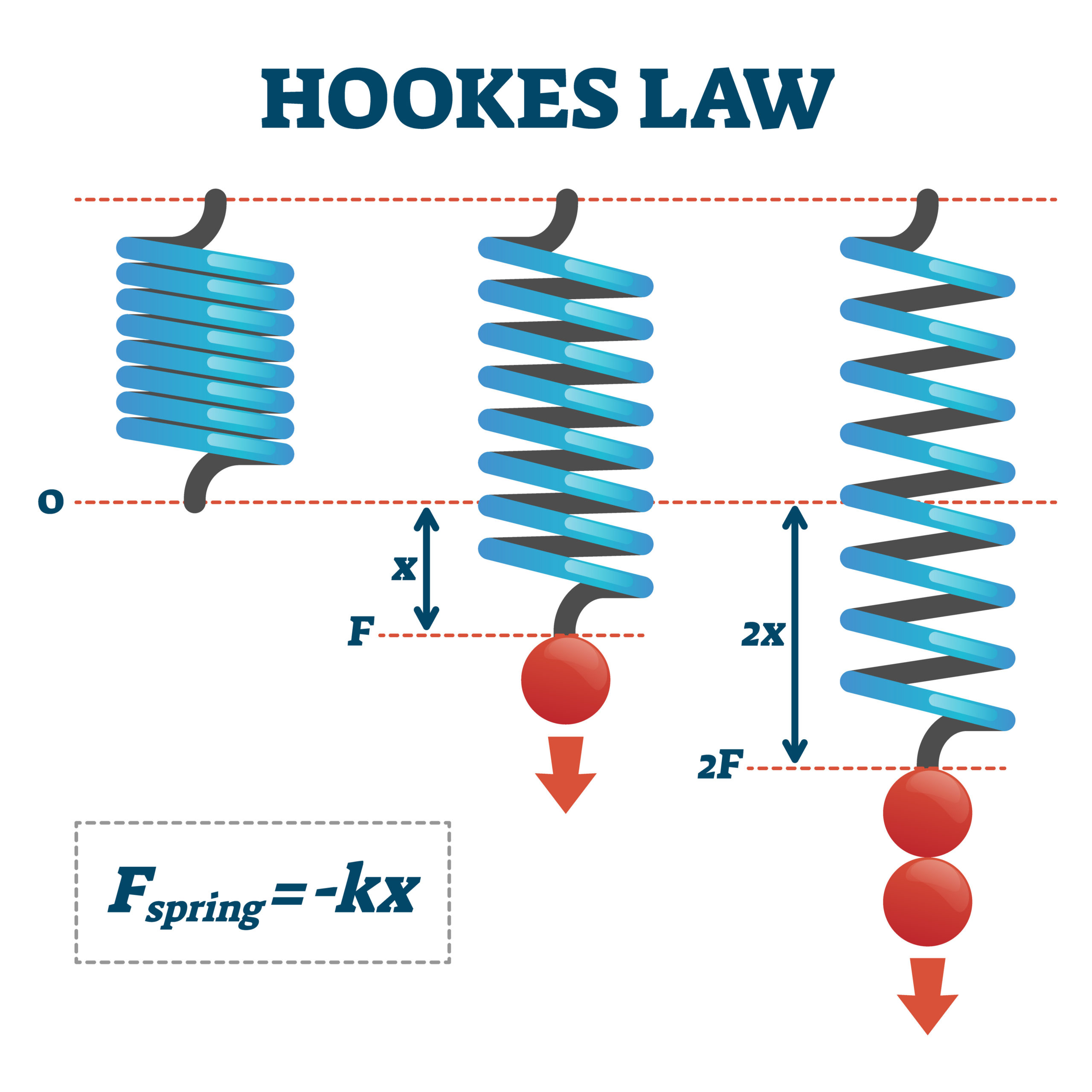
Youngs modulus E or Y is a measure of a solids stiffness or resistance to elastic deformation under load. The restoring force which tries to restore the deformation of spring can be expressed by Hookes law which is F_s k x the negative sign shows that the force is acting against the displacement x. An objects mass also determines the strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies.
This is where. In physics a fluid is a liquid gas or other material that continuously deforms flows under an applied shear stress or external force. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram kg.
It deals with the case of linear elastic materialsFollowing this discovery this type of equation often called a stress-strain relation in this example but also called a constitutive assumption or an equation of state was. An object that compresses or stretches a spring is always acted upon by a force that restores the object to its rest or equilibrium position. Where F is the force x is the extension in length and k is the constant of proportionality known as the spring constant in Nm.
A microphone colloquially called a mic or mike m aɪ k is a transducer that converts sound into an electrical signalMicrophones are used in many applications such as telephones hearing aids public address systems for concert halls and public events motion picture production live and recorded audio engineering sound recording two-way radios megaphones and radio and. The proportionality of limit is the maximum stress that a material can hold without the departure from a linear stress-strain relation. Spring constant can be calculated using Hookes Law.
Moment of force has the units newton-meters Nm. A body with this ability is said to behave or respond elastically. The law is named after 17th-century.
Mass is the quantity of matter in a physical bodyIt is also a measure of the bodys inertia the resistance to acceleration change of velocity when a net force is applied. The proportionality constant k is the spring constant. To measure the spring constant of a spring using two different methods.
Hookes law is valid only in this linear part of the stress-strain curve. Mechanical properties of matter. Hookes Law is a principle of physics that states that the that the force needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance is proportional to that distance.
Hookes law also referred to as the law of elasticity was discovered by an English scientist named Robert Hooke in the year 1660. For most springs specifically for those that are said to obey Hookes Law the magnitude of the force is directly proportional to the amount of stretch or compression of the spring. Position x is not the part of any derivative nor is it raised to any power.
Hookes Law states that the strain of the material is proportional to the applied stress within the elastic limit of that material. Physics science that deals with the structure of matter and the interactions between the fundamental constituents of the observable universe. Physical restrictions on the form of the constitutive relations can be applied by requiring that the second law of thermodynamics be satisfied under all conditions.
To a greater or lesser extent most solid materials exhibit elastic behaviour but there is a limit to the magnitude of the force and the accompanying deformation within. Plasma is typically an electrically quasineutral medium of unbound positive and negative. The slope of the linear curve gives Youngs modulus of the material.
As per the Hookes Law if spring is stretched the force exerted is proportional to the increase in length from the equilibrium length. Let us define the basic hookes law that gives us the definition of the spring constant. Mathematically Hookes law is commonly expressed as.
In fluids non-newtonian fluids to be. They have zero shear modulus or in simpler terms are substances which cannot resist any shear force applied to them. Fluid statics or hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies the condition of the equilibrium of a floating body and submerged body fluids at hydrostatic equilibrium and the pressure in a fluid or exerted by a fluid on an immersed body.
The point A is termed as Limit of Proportionality.
The Physics Of Springs How Manufacturers Understand Spring Design
Biomeca Understanding Elastic Properties Of The Skin

Hooke S Law Gcse Physics Combined Edexcel Revision Study Rocket

Physics 151 Week 12 Day Topics Hooke S Law And Oscillations Chs 8 14 Springs Hooke S Law Applications Oscillations Period Frequency Ppt Download
Comments
Post a Comment